2x3 Wood Beam Span Calculator - Deflection and Load Analysis
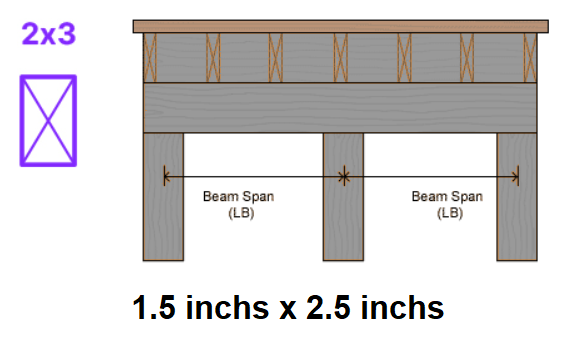
2x3 Wood Beam Overview
2x3 Wood Beam is a compact lumber size commonly used for smaller construction projects, furniture, and lightweight framing. Below are its key details:
- Nominal Size: 2 inches × 3 inches
- Actual Size: Typically 1.5 inches × 2.5 inches (38mm × 64mm)
- Materials: Made from softwood (e.g., pine, spruce) or hardwood (e.g., birch, maple).
- Applications:
- Framing for small structures
- Furniture and cabinetry
- Shelving and storage solutions
- DIY projects and crafts
- Advantages: Lightweight, easy to handle, and cost-effective for smaller projects.
- Limitations: Limited structural strength and not suitable for heavy-duty applications.
2x3 wood beams are ideal for projects where space, weight, and budget are key considerations, offering flexibility for a range of light-duty tasks.
Deflection of a Wood Beam Formula
To calculate the deflection of a wood beam with a rectangular cross-section, use the following formula:
\[ \delta = \frac{5 \cdot w \cdot L^4}{384 \cdot E \cdot I} \]
Where:
- \(\delta\) (Deflection):
- The deflection at the midspan of the wood beam in inches.
- \(w\) (Uniform Load):
- The uniformly distributed linear load applied to the beam, in pound-force per inch (lbf/in).
- \(L\) (Beam Span):
- The span or unbraced length of the beam in inches.
- \(E\) (Modulus of Elasticity):
- The modulus of elasticity of the wood species used, in pounds per square inch (psi).
- \(I\) (Moment of Inertia):
- The area moment of inertia of the beam's cross-section, in inches to the fourth power (in\(^4\)).
We calculate the area moment of inertia (\(I\)) of the beam's cross-section using this formula:
\[ I = \frac{b \cdot d^3}{12} \]
Where:
- \(I\):Area moment of inertia in inches to the fourth power (in\(^4\)).
- \(b\):Actual base width or thickness of the lumber in inches.
- \(d\):Actual height of the lumber in inches.
To calculate the actual bending stress, we use this formula:
\[ f_b = \frac{M}{S} \]
Where:
- \(f_b\):Bending stress in pounds per square inch (psi).
- \(M\):Bending moment in pound-force inches (lbf·in).
- \(S\):Section modulus in cubic inches (in\(^3\)).
The bending moment \(M\) is calculated as:
\[ M = 1/8 (\cdot w \cdot L^2) \]
Where:
- \(w\):Uniformly distributed load in pound-force per inch (lbf/in).
- \(L\):Beam span or unbraced length in inches.
The shear force \(V\) is calculated as:
\[ V = \cdot w \cdot L / 2 \]
We calculate the actual shear stress (\(f_v\)) by dividing the shear force by the cross-sectional area of the beam:
\[ f_v = \frac{V}{A} \]
Where:
- \(f_v\):Shear stress in pounds per square inch (psi).
- \(V\):Shear force in pound-force (lbf).
- \(A\):Cross-sectional area of the beam in square inches (in\(^2\)).
Wood Species - Modulus of Elasticity (E ×106 psi)
| Species | No. 1 | No. 2 | No. 3 | Stud | Const. | Standard | Utility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alaska Cedar | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.0 |
| Alaska Spruce | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.1 |
| Alaska Yellow Cedar | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
| Beech-Birch-Hickory | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.2 |
| Coast Sitka Spruce | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.2 |
| Douglas Fir-Larch | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.3 |
| Douglas Fir-Larch (North) | 1.8 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.3 |
| Douglas Fir-South | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.0 |
| Eastern Hemlock-Balsam Fir | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.8 |
| Eastern White Pine | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.8 |
| Hem-Fir | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.1 |
| Hem-Fir (North) | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.3 |
| Mixed Maple | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 0.9 |
| Mixed Oak | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Mixed Southern Pine | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.1 |
| Northern Red Oak | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.0 |
| Northern White Cedar | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Norway Spruce (North) | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
| Red Maple | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.2 |
| Red Oak | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.0 |
| Redwood | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 |
| Southern Pine | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| Spruce-Pine-Fir | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.1 |
| Spruce-Pine-Fir (South) | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| Western Cedars | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| White Oak | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Yellow Cedar | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.1 |
 Home
Home Back
Back